CRESC Annual Conference 2011 – Framing the City
The CRESC annual conference 2011 ‘Framing the City’ is now taking place from today, 07 September through to Friday 09 September in Manchester at the Royal Northern College of Music. It is organised by Sophie Watson (Chair), Gillian Evans, Elizabeth Silva and Alban Webb.
Key note speakers include: Ian Sinclair, author of London Orbital and London: City of Disappearances; Alistair Bonnett, author of Left in the Past: Radicalism and the Politics of Nostalgia; Maria Kaika author of City of Flows; Roselund Lennart, author of Exploring the City with Bourdieu: Applying Pierre Bourdieu?s theories and methods to study the community; Talja Blokland, author of Urban Bonds and co-editor of Networked Urbanism; Nick Couldry author of Why Voice Matters Culture and Politics After Neoliberalism.
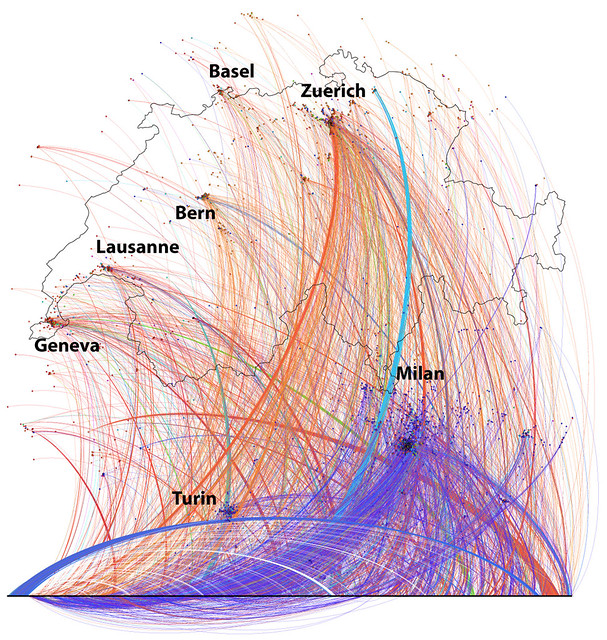
Image by urbanTick for NCLn / Location based social network based on Twitter data collected in central Europe focusing on Switzerland. Colours indicating message language. The main languages are, Italian=blue, English=orange, French=red, German=green.
The bottom line are external nodes for which we have no location information.
I will be presenting today at the conference in a session called ‘Change and Moulding’ in the afternoon. The paper New City Landscapes and Virtual Urban Social Networks is looking at how physical elements are shaping the virtual world. In detail this is how physical aspects of the location can be found as influencing parameters of the virtual description. Overall this forms an argument as to why and how digital social networking data can be useful for decision making and planning.
Increasingly people use digital or online networks to communicate and interact. This changes the social scape of the urban area and with it the interactive hot spots change and fluctuate throughout the city as individuals follow the narrative path of their everyday routines. People leave messages, distribute news and respond to conversations not only in traditional locations anymore but potentially anywhere in the city.
This paper discusses the emerging potential of social media data used for urban area research and city planning. Also aspects of visualisation as well as privacy and ethical implications are discussed. The information gathered from social media networks usually can be associated with a physical location for example via the GPS of the smart phone. For this virtual social infrastructure mapping project, the data is derived from the Twitter micro blogging service.
The data is mapped as a virtual landscape on top of the real landscape connecting it via the common place names. At the same time the data is used to visualize the social network across these virtual-real places and in this way can make visible the places were people link the virtual and the real world in urban areas around the globe.
