 |
Conceptual model for integrating social
and physical constructs to monitor,
analyze and model slums. |
Continuing our research on slums, we have just had a paper published in the journal Regional Studies, Regional Science entitled “The Study of Slums as Social and Physical Constructs: Challenges and Emerging Research Opportunities“. In this open access publication we review past lines of research with respect to studying slums which often focus on one of three constructs: (1) exploring the socio-economic and policy issues; (2) exploring the physical characteristics; and, lastly, (3) those modelling slums. We argue that while such lines of inquiry have proved invaluable with respect to studying slums, there is a need for a more holistic approach for studying slums to truly understand them at the local, national and regional scales. Below you can read the abstract of our paper:
“Over 1 billion people currently live in slums, with the number of slum dwellers only expected to grow in the coming decades. The vast majority of slums are located in and around urban centres in the less economically developed countries, which are also experiencing greater rates of urbanization compared with more developed countries. This rapid rate of urbanization is cause for significant concern given that many of these countries often lack the ability to provide the infrastructure (e.g., roads and affordable housing) and basic services (e.g., water and sanitation) to provide adequately for the increasing influx of people into cities. While research on slums has been ongoing, such work has mainly focused on one of three constructs: exploring the socio-economic and policy issues; exploring the physical characteristics; and, lastly, those modelling slums. This paper reviews these lines of research and argues that while each is valuable, there is a need for a more holistic approach for studying slums to truly understand them. By synthesizing the social and physical constructs, this paper provides a more holistic synthesis of the problem, which can potentially lead to a deeper understanding and, consequently, better approaches for tackling the challenge of slums at the local, national and regional scales.”
Keywords: Slums; informal settlements; socio-economic; remote sensing; crowdsourced information; modelling.
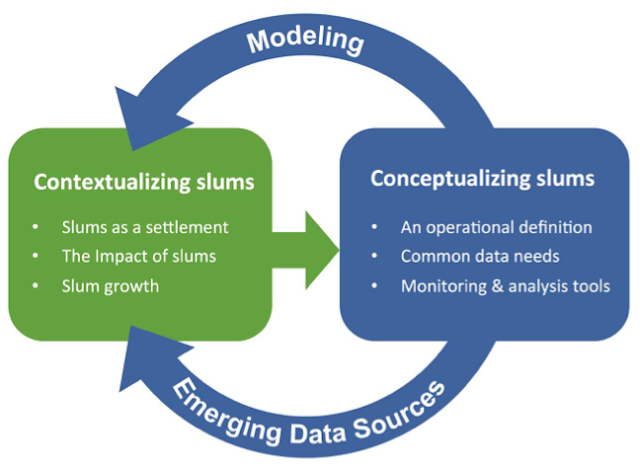 |
| Framework for studying and understanding slums. |
We hope you enjoy this paper and we wound be interested in receiving any feedback.
Full Reference:
Mahabir, R., Crooks, A.T., Croitoru, A. and Agouris, P. (2016), “The Study of Slums as Social and Physical Constructs: Challenges and Emerging Research Opportunities”, Regional Studies, Regional Science, 3(1): 737-757. (pdf)
Continue reading »










