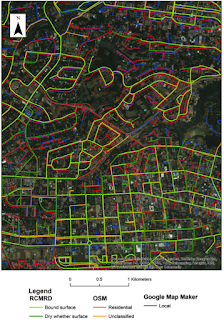
The motivation behind the paper was that while there are numerous studies comparing VGI to authoritative data in the developed world, there are very few that do so in developing world. In order to address this issue in the paper we compare the quality of authoritative road data (i.e. from the Regional Center for Mapping of Resources for Development – RCMRD) and non-authoritative crowdsourced road data (i.e. from OpenStreetMap (OSM) and Google’s Map Maker) in conjunction with population data in and around Nairobi, Kenya.
Results from our analysis show variability in coverage between all these datasets. RCMRD provided the most complete, albeit less current, coverage when taking into account the entire study area, while OSM and Map Maker showed a degradation of coverage as one moves from central Nairobi towards more rural areas. Further information including the abstract to our paper, some figures and full reference is given below.
Abstract:
With volunteered geographic information (VGI) platforms such as OpenStreetMap (OSM) becoming increasingly popular, we are faced with the challenge of assessing the quality of their content, in order to better understand its place relative to the authoritative content of more traditional sources. Until now, studies have focused primarily on developed countries, showing that VGI content can match or even surpass the quality of authoritative sources, with very few studies in developing countries. In this paper we compare the quality of authoritative (data from the Regional Center for Mapping of Resources for Development – RCMRD) and non-authoritative (data from OSM and Google’s Map Maker) road data in conjunction with population data in and around Nairobi, Kenya. Results show variability in coverage between all these datasets. RCMRD provided the most complete, albeit less current, coverage when taking into account the entire study area, while OSM and Map Maker showed a degradation of coverage as one moves from central Nairobi towards rural areas. Furthermore, OSM had higher content density in large slums, surpassing the authoritative datasets at these locations, while Map Maker showed better coverage in rural housing areas. These results suggest a greater need for a more inclusive approach using VGI to supplement gaps in authoritative data in developing nations.
Keywords: Volunteered Geographic Information; Crowdsourcing; Road Networks; Population Data; Kenya
 |
| Road Coverage per km2 |
 |
| Pairwise difference in road coverage. Clockwise from top left: i) RCMRD 2011 versus Map Maker 2014; ii) RCMRD 2011 versus OSM 2011; iii) RCMRD 2011 versus OSM 2014; iv) OSM 2014 versus Map Maker 2014 (Red cells: first layer has higher coverage; Green cells: second layer has higher coverage). |
Full Reference:
Mahabir, R., Stefanidis, A., Croitoru, A., Crooks, A.T. and Agouris, P. (2017), “Authoritative and Volunteered Geographical Information in a Developing Country: A Comparative Case Study of Road Datasets in Nairobi, Kenya”, ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 6(1): 24, doi:10.3390/ijgi6010024.
As always any thoughts or comments about this work are welcome.
Continue reading »